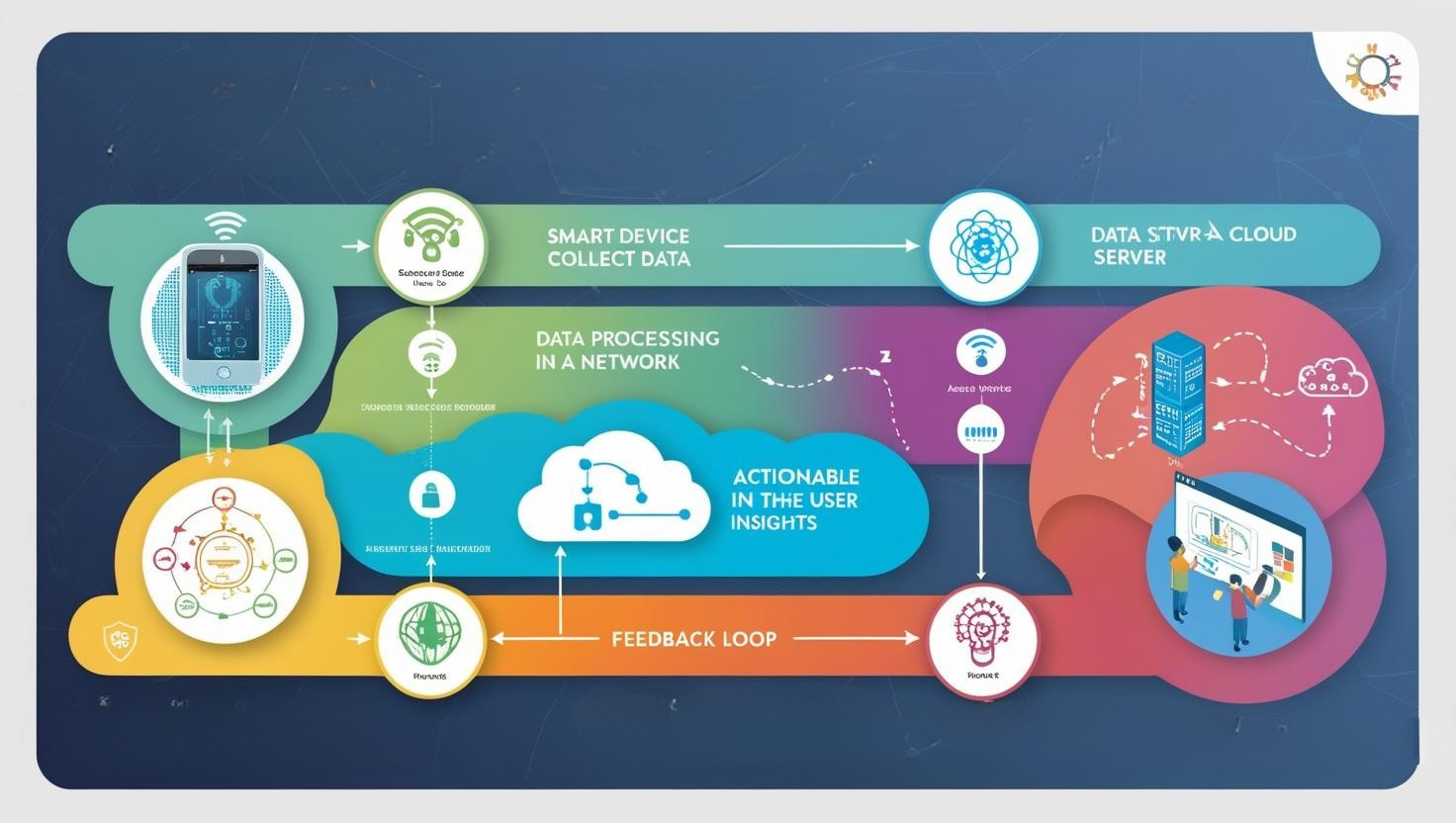
Device/Thing: Physical objects are equipped with embedded sensors, software, and other technologies to collect and transmit data.
Connectivity: The devices connect to the internet or local networks through wireless protocols
Data Collection: Sensors on the IoT devices collect data from the environment
Data Transmission: The collected data is sent to a central platform or cloud for storage and further processing.
Data Processing: The cloud platform or local servers analyze the data, often using machine learning or algorithms to derive insights or trigger actions.
Action: Based on the analysis, the system takes actions, such as sending alerts, activating devices, or updating settings.
User Interface: End-users can access IoT data through apps, dashboards, or notifications for monitoring or control.
Feedback Loop: IoT systems may continuously monitor and adjust, creating a feedback loop that improves performance or responds to new inputs.
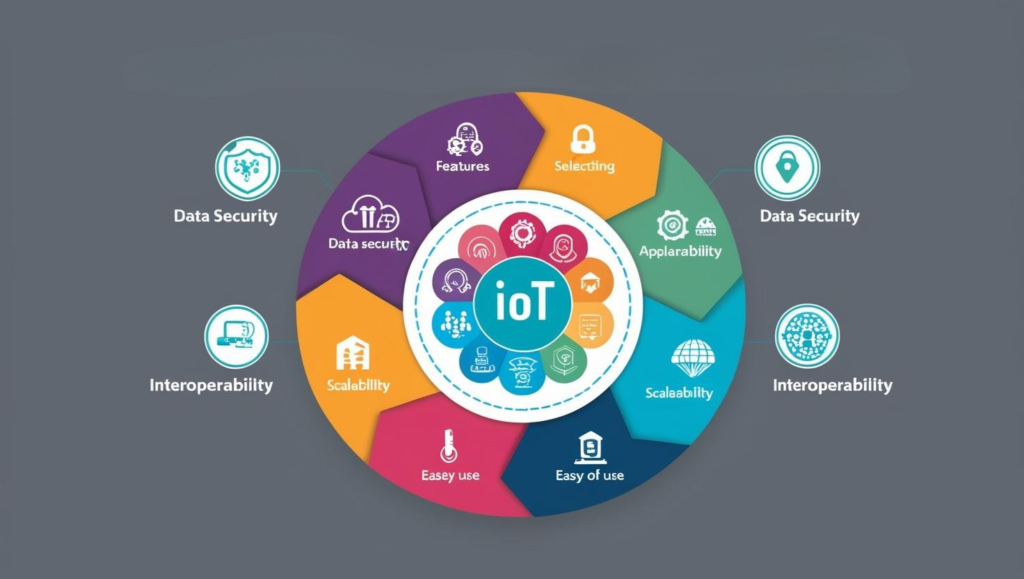
Enables data exchange and communication.
Collect real time data & Perform action
Gathers large amount of data & Provide insights and optimize processes
Device work across different platform & Seamless integration with other systems.
Can easily expand by adding new devices & supports both small and large deployment
Process data instantly for immediate actions & provide real time updates and alerts
Low power consumption for long lasting performance & cost effective and sustainable
Protection from unauthorize access. Ensures user privacy and data security
